| [1]Laure B,Besnier JM,Bergemer-Fouquet AM,et al.Effect of hydroxyapatite coating and polymethylmethacrylate on stainless steel implant-site infection with Staphylococcus epidermidis in a sheep model.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008; 84(1):92-98.
[2]Trampuz A,Widmer AF.Infections associated with orthopedic implants. Curr Opin Infect Dis.2006;19(4):349-356.
[3]Harris LG,Richards RG.Staphylococci and implant surfaces: a review. Injury.2006;37 Suppl 2:S3-S14.
[4]Gristina AG,Naylor PT,Myrvik QN. Mechanisms of musculoskeletal sepsis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1991;22(3): 363-371.
[5]王晓静,王国伟,赵铱民.金黄色葡萄球菌在不同种植体表面涂层粘附情况的体外实验研究[J].中国口腔种植学杂志, 2009,14(2):16.
[6]朱梓园,张富强,郑学斌.含银抗菌羟基磷灰石涂层银离子的缓释性能[J].上海口腔医学, 2009,18(1):66-68.
[7]佘文珺,张富强,胡滨,等.载银抗菌基托树脂银离子的缓释性研究[J].口腔医学, 2007,27(7):340-342.
[8]Shirkhanzadeh M.Bioactive calcium phosphate coatings prepared by electrodeposition. Journal of materials science letters,1991;10(23):1415-1417.
[9]Zhang J,Lin C,Feng Z,et al.Electrochemical preparation for bioactive ceramics coating on Ti-6Al-4V substrate.Chem J Chinese U.1997;18:961-962.
[10]张建民,林昌健.电沉积磷酸钙生物活性陶瓷[J].物理化学学报, 1998,14(8):698-703.
[11]张建民,石秋芝,杨长春,等.电流密度对钙磷沉积层组成和结构的影响[J].化学研究,2002,13(2):5-7.
[12]赵中伟,陈爱良,陈星宇,等.脉冲阴极电沉积羟基磷灰石涂层[J].中国有色金属学报,2005,15(12):2023-2027.
[13]王英波,鲁雄,赵婧,等. 脉冲电化学沉积制备 n-HA/ZrO2 复合涂层[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2009,38(6):1071-1075.
[14]张柏林.电化学方法制备钛基纳米银/羟基磷灰石复合涂层及其相关性质研究[D].西南交通大学,2010.
[15]Kim H,Kokubo T,Fujibayashi S,et al.Bioactive macroporous titanium surface layer on titanium substrate.J Biomed Mater Res.2000;52(3):553-557.
[16]Lu X,Wang Y,Yang X,et al. Spectroscopic analysis of titanium surface functional groups under various surface modification and their behaviors in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res A.2008;84(2):523-534.
[17]Legeros RZ,Legeros JP.Calcium phosphate bioceramics: past, present and future. Key Eng Mater.2002;240:3-10.
[18]卢旻鹏,蒋电明,权正学,等.载银纳米抗菌复合骨填充材料体外抗菌及缓释性能研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(6): 691-695.
[19]Casemiro LA,Martins CHG,Pires-de-Souza FDC,et al.Antimicrobial and mechanical properties of acrylic resins with incorporated silver--zinc zeolite--part I. Gerodontology. 2008;25(3):187-194.
[20]Lee BU,Yun SH,Ji JH,et al.Inactivation of S.epidermidis,B.subtilis,and E.coli bacteria bioaerosols deposited on a filter utilizing airborne silver nanoparticles.J Microbiol Biotechnol.2008;18(1):176-182.
[21]Panácek A,Kolár M,Vecerová R,et al.Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles against Candida spp.Biomaterials. 2009;30(31):6333-6340.
[22]Matsui Y,Otomo K,Ishida S,et al.Effect of silver-carrying photocatalyst “Hikari-Gintech”on mycobacterial growth in vitro. Microbiol Immunol.2004;48(7): 489-495.
[23]Cardoso RF,Cooksey RC,Morlock GP,et al.Screening and characterization of mutations in isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates obtained in Brazil. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2004;48(9):3373-3381.
[24]Sun RW,Chen R,Chung NP,et al.Silver nanoparticles fabricated in hepes buffer exhibit, cytoprotective activities toward HIV-1 infected cells.Chem Commun.2005;(40): 5059-5061.
[25]Lu L,Sun RW,Chen R,et al.Silver nanoparticles inhibit hepatitis B virus replication.Antivir Ther.2008;13(2): 253-262.
[26]张若愚,夏雪山,胡亮,等.Ag/Diatomite复合材料及其对禽流感病毒的杀灭研究[J].贵金属,2004,25(2):28-32.
[27]Lok CN,Ho CM,Chen R,et al.Proteomic analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles.J Proteome Res. 2006;5(4):916-924.
[28]Welz B.原子吸收光谱法:第二次全修订版[M].李家熙等译.北京:地质出版社,1989.
[29]马怡载.石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法[M].北京市:原子能出版社, 1989.
[30]Liau SY,Read DC,Pugh WJ,et al.Interaction of silver nitrate with readily identifiable groups: relationship to the antibacterial action of silver ions. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1997; 25(4):279-283.
[31]Kawahara K,Tsuruda K,Morishita M,et al.Antibacterial effect of silver-zeolite on oral bacteria under anaerobic conditions. Dent Mater.2000;16(6):452-455.
[32]常涛.银离子消毒剂研究概述[J].解放军预防医学杂志, 2005, 23(1):75-77.
[33]Qu F,Xu H,Wei H,et al.Effects of pH and Temperature on Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles[R]. Yantai: Computer Science of Yantai University, 2010:2033-2037.
[34]Dong Y,Li X,Tian L,et al.Towards long-lasting antibacterial stainless steel surfaces by combining double glow plasma silvering with active screen plasma nitriding.Acta Biomaterialia. 2011;7(1):447-457.
[35]Matsumura Y,Yoshikata K,Kunisaki S,et al.Mode of bactericidal action of silver zeolite and its comparison with that of silver nitrate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69: 4278-4281.
[36]阮洪江,范存义,郑学斌,等.载银羟基磷灰石抗菌涂层抗菌性能及对成骨细胞影响的体外实验[J].科学通报,2009,54(1):60-66. |

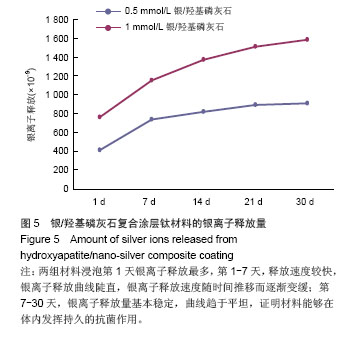
.jpg)